E-bikes are not, as you might think, a new idea. In fact, the first e-bikes (or ‘cycling machines’) were invented as long ago as the 1800’s!
However, as the huge batteries and motors used at the time made them extremely inefficient, it took until the 1990’s for technology to catch up with the concept in a viable way.
Today’s e-bikes, whilst far zippier than the original Victorian invention, are essentially based on the same simple idea – a motor, a battery and a controller, (and a few other bits!), working in unison to provide a fun and easy way of getting about!
Let’s talk about each component to see how they work together, to create the bike that anyone can use…
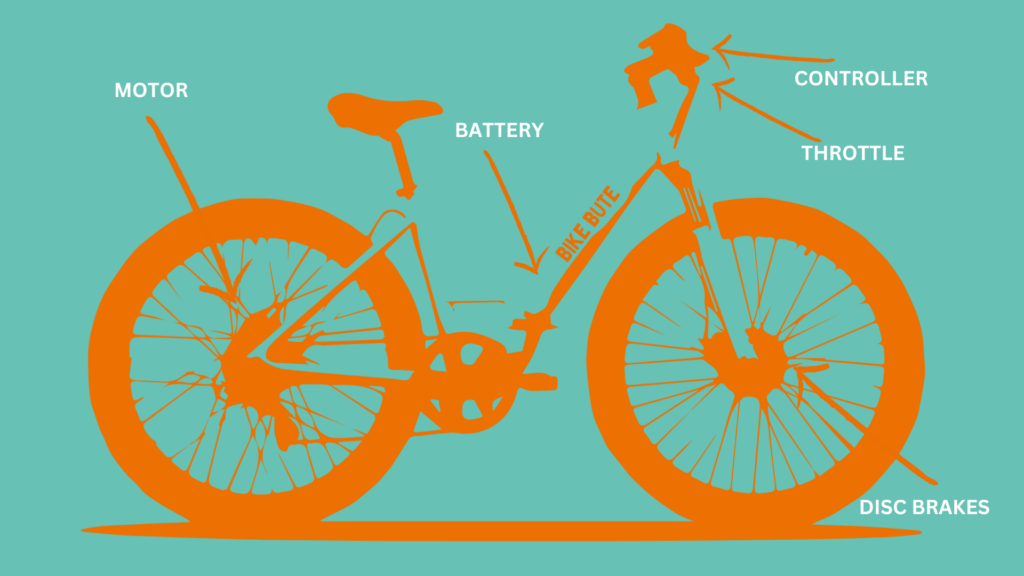
Electric Motor
The electric motor is the HEART of an e-bike. It’s what provides the power to assist the rider and is usually found in the front or rear wheel hub of the bike. It switches on when the rider begins pedalling and reduces the level of effort needed to propel the bike.
The electric motor is powered by a battery, which you’ll usually find located in the centre, or the rear wheel of the bike.
Battery


As the POWER SOURCE for the electric motor, the battery (usually lithium-ion) makes the magic happen! Whilst lithium-ion batteries are more expensive than lead-acid batteries, they also have a much longer lifespan and they can be charged more quickly – important if you’re using your e-bike every day!
So how does all this power get to the right places? For that, we need a controller…
Controller
The controller is the BRAIN of the e-bike, and, true to its name, controls the electric motor. It’s actually the component that takes the energy from the battery and directs it to the motor according to the user and sensor inputs. It monitors battery voltage, bike speed, motor power, and pedalling activity.
But how does the controller know when to ‘kick in’?

Pedal Assist Sensor
In order to detect when the rider is pedalling, the e-bike needs a sensor. The pedal-assist sensor sends a signal to the controller, which in turn, starts the electric motor.
Of course, we need to know how much power is left when we’re riding, and we do this from the display screen.
Display

The display is the FEEDBACK MECHANISM of an e-bike, which is located on the handlebars.
It’s a small screen that shows the rider the battery level, the current speed, and the level of assistance, and can be used to control the level of assistance the rider requires.
Throttle
Located on the handlebars of the bike, is the throttle; a lever that can be used to provide those little bursts of power that might be needed, for example, when cycling up a steep hill or when you’re flagging on a slow incline. The rider’s weight can also be a factor, as the heavier the rider, the more power is needed to propel the bike forward.
Brakes
E-bikes need brakes just like regular bikes, and these are typically disc brakes, which are more powerful than rim brakes and are more effective when riding in wet conditions.
So there you have it – your first basic e-bike anatomy lesson!
But whilst understanding how they work may be useful, knowing the benefits of an e-bike is essential to encouraging more people to use them in their everyday lives, whether for work, for fitness or simply for leisure.
Why e-bikes are important for the planet
Besides being fun to use – and easier to ride than mechanical bikes – e-bikes play a crucial role in helping us to live more sustainably.
- For one, they produce zero emissions, which helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Every trip on a bike, instead of a car, is another step towards a healthier planet!
- Using an e-bike will also help to reduce traffic congestion, which is why they are so popular in cities. Slipping past queries of cars on a workday is also really satisfying!
- E-bikes help to improve air quality; wherever there are cars, people or industry, using an e-bike means that you are making green choices, and reducing the emissions being released into our atmosphere.
- Importantly, e-bikes also require far less energy to produce than a car and emit fewer carbon emissions in the manufacturing process.
- …and no matter where you live, by switching from driving to cycling, you will help to reduce the noise pollution that can have such a detrimental effect on physical and mental health.
Join the Green Revolution!

E-bikes are fast becoming a viable means of sustainable transport in the UK, with bike sales having almost tripled in the past five years from 55,000 in 2017 to around 155,000 in 2022.
The trend is steadily growing, as this genial invention of almost 130 years ago is being increasingly recognised – not only for its green potential, but also for its benefits to health and wellbeing.
So, now that you know how an e-bike works, and what it can do for you and the planet, why not consider giving one a try? We think you’ll be hooked from the first surprisingly easy hill!
Bike Bute is Scotland’s first island community bike scheme, and serves Isle of Bute community and visitors to the island. The charity is part of Fyne Futures, which aims to inspire, educate and empower people to live sustainably on the Isle of Bute.
Visit Bute and explore all that the island has to offer – by bike!
